Synaxis.
Maroneia. Aghios Charalambos.
THRACE
84
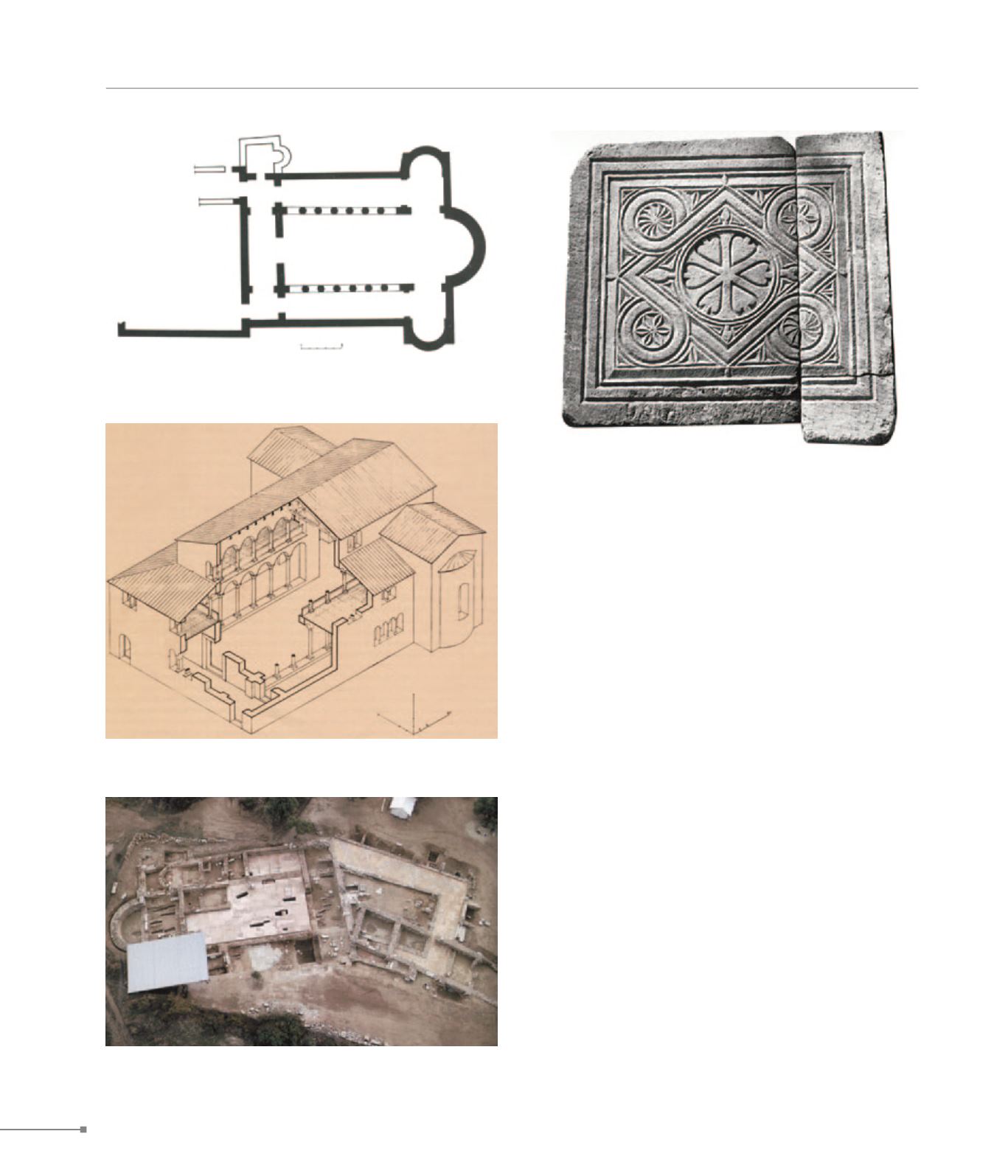
9. Synaxis, basilica, ground plan (Σύναξη, κάτοψη της βασιλικής)
9. Synaxis, reconstruction of the basilica (Σύναξη, αναπαράσταση της
βασιλικής)
9. Synaxis, closure slab (Σύναξη, θωράκιο)
9.
Synaxis.
Close to the coast of the Thracian Sea, at the Synaxis site, 10 km
E of Maroneia a three-aisled Early Christian basilica has been
excavated. It has a transept, a narthex, an atrium and a chapel.
The building material used for this complex probably originates
from the sanctuary of Maron, of Roman origin, which had been
established here; the floors were decorated with mosaics. The
basilica was destroyed and abandoned in the 7th c. Over its ruins
and with its building material, a Mid-Byzantine monastery was
founded; it was abandoned in the mid-13th c. At a short distance
from this Christian church complex was excavated a Roman pe-
riod complex, which was identified as a guesthouse for pilgrims
on their way to Samothrace. The complex was in use until the
6th c. and was definitively abandoned after the 7th c.
10.
Aghios Georgios.
Ancient defensive walls survive, on which alterations of the Ear-
ly Christian or Byzantine period have been identified.
11.
Maroneia. Aghios Charalambos.
An archdiocesan seat since the Early Christian period, in the
14th c. Maroneia was raised to a metropolis. It came under
Turkish domination in 1373 at the earliest. Early Christian and
Byzantine construction was restricted to the coastal end of the
11. Maroneia, Paliochora, basilica (Μαρώνεια, Παλιόχωρα, βασιλική)


